The Healthcare IoT market is witnessing remarkable growth, with global revenue projected to reach US$93.28 billion by 2025. At the heart of this transformation are IoT-powered health apps, reshaping how patients, doctors, and caregivers interact with medical data. From real-time monitoring of vital signs to personalized treatment plans, these apps enhance accessibility, efficiency, and preventive care.
Whether managing chronic conditions, tracking fitness goals, or ensuring medication adherence, IoT integration bridges the gap between technology and well-being. With advancements in AI, 5G, and next-generation wearables, the future of connected healthcare looks more promising than ever. In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits of IoT-enabled health apps, challenges in IoT-driven health apps, a step-by-step guide to building them, and key future trends shaping digital healthcare.
The Role of Wearables in Modern Healthcare

Wearables are no longer just fitness gadgets—they’ve become vital tools in monitoring health and supporting wellness. From everyday users to patients managing chronic conditions, these devices provide real-time insights that enhance decision-making for both individuals and healthcare professionals. Their growing presence highlights how technology is reshaping preventive care and personal health management.
Common Types of Wearables (Fitness Trackers, Smartwatches, Medical-grade Devices)

Wearables range from popular fitness trackers that monitor steps and calories to advanced smartwatches that track multiple health metrics. In addition, medical-grade wearables are now being used to monitor heart conditions, glucose levels, and other critical data for clinical use.
Key Data They Collect (Heart Rate, Sleep, Activity Levels, Glucose Levels, Etc.)
Modern wearables capture a wide variety of data, including heart rate, blood oxygen levels, sleep quality, activity levels, and even stress indicators. Some specialized devices go further, measuring glucose, ECGs, or blood pressure, offering users and doctors actionable health insights.
Growing User Adoption And Trust In Wearable Technology
As wearables have proven more reliable and accessible, user adoption continues to grow worldwide. People trust these devices not only for fitness but also for managing chronic conditions and preventive care. The Fitbit & Apple Health app tracks steps, heart rate, sleep, and activity, syncing data across multiple devices for holistic health monitoring.
Here are 6 relevant statistics related to IoT in healthcare apps:
- IoT adoption in healthcare is expected to reach 87% by 2025, showing widespread integration across the sector.
- Approximately 60% of healthcare organizations are already using IoT devices for monitoring and data collection.
- IoT-enabled remote patient monitoring has been shown to reduce hospital readmissions by 45%.
- The use of IoT in healthcare has resulted in a 50% reduction in patient wait times.
- Healthcare facilities using IoT technology report an average operational cost reduction of 26%.
Benefits of IoT-Enabled Health Apps

IoT-enabled health apps are transforming healthcare by providing real-time insights and continuous monitoring. They empower patients to take control of their health while enabling doctors to make data-driven decisions. Below are the key benefits of IoT-enabled health apps:
- Personalized insights – IoT health apps deliver customized recommendations by analyzing real-time wearable data, ensuring unique, user-specific wellness guidance daily.
- Remote monitoring – Healthcare providers can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs remotely, reducing hospital visits and enabling timely, proactive medical interventions effectively.
- Early detection – Continuous IoT tracking identifies potential health risks earlier, allowing preventive action and timely treatment before conditions worsen significantly, saving lives.
- Improved patient engagement – Interactive health apps motivate users to track fitness, sleep, nutrition, and activity, empowering consistent self-care and overall healthier lifestyles.
- Data-driven decisions – Doctors and caregivers rely on real-time IoT data, enabling accurate, informed, and timely medical decisions for personalized treatments.
- Holistic wellness tracking – IoT health apps unify fitness, stress, sleep, and vital health metrics into one platform, providing complete lifestyle insights.
Challenges in IoT-Driven Health Apps
IoT-driven health apps provide significant opportunities for remote monitoring and personalized care, but they also face several challenges. Below are the key obstacles affecting their development and adoption:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Data privacy and security concerns (HIPAA, GDPR compliance) | Protecting sensitive health data from breaches while ensuring compliance with strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. |
| Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of sensor data | Maintaining consistent, high-quality readings from IoT sensors to support correct diagnoses and health monitoring. |
| Interoperability across devices and platforms | Enabling seamless data exchange between different IoT devices, apps, and healthcare systems without compatibility issues. |
| User adoption and device fatigue | Encouraging users to consistently engage with devices and apps while avoiding drop-offs caused by complexity or overuse. |
| High development and maintenance costs | Building IoT-driven health apps requires significant investment in hardware integration, software updates, and ongoing support. |
| Battery life and connectivity issues | Devices often face challenges with limited battery capacity and unreliable internet connectivity, which can affect continuous monitoring. |
Step-by-Step Guide to Develop IoT-Integrated Health Apps
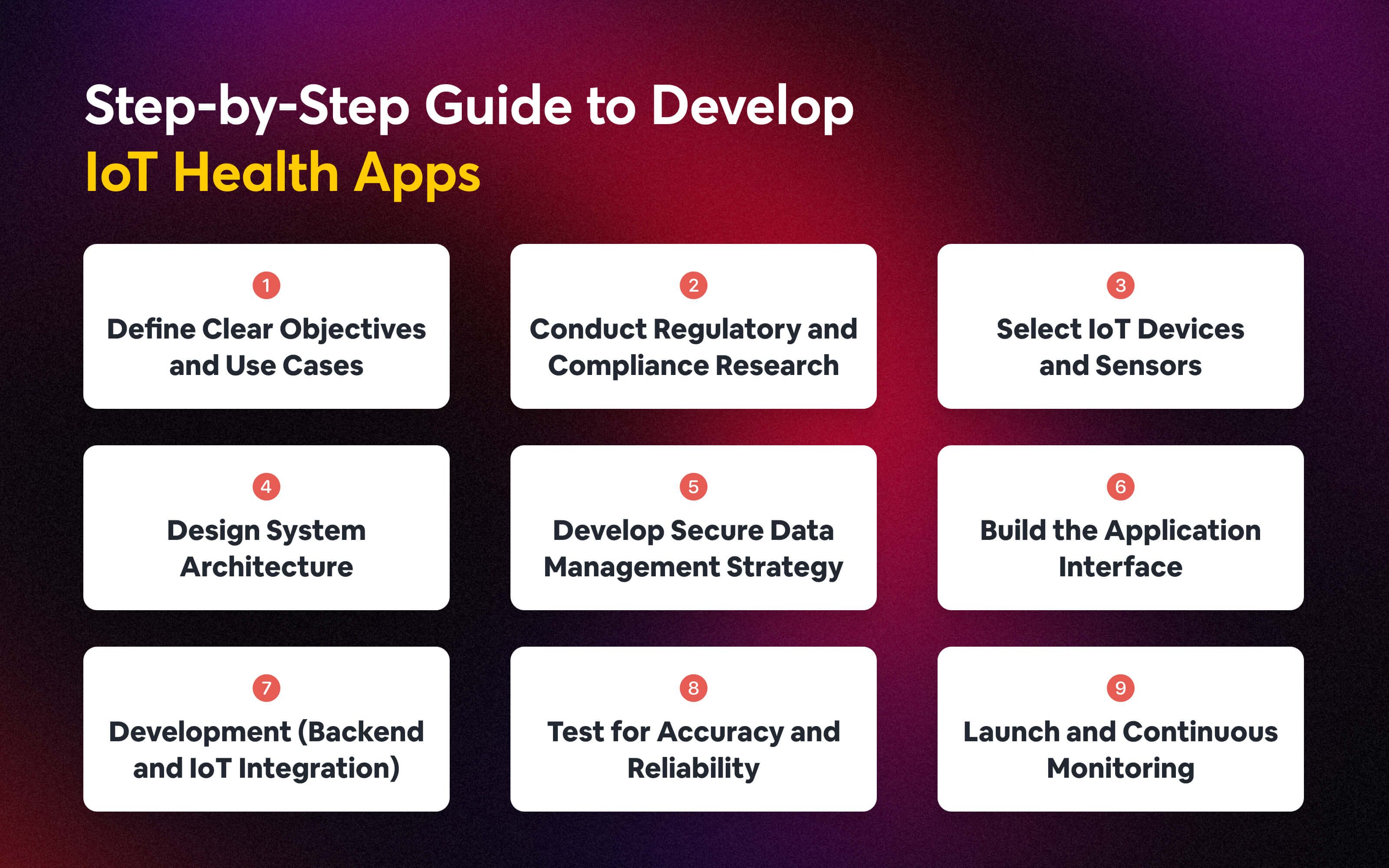
Developing IoT-integrated health apps requires careful planning, seamless device connectivity, and robust data management. These apps combine wearables, sensors, and healthcare systems to provide real-time insights and personalized care. The following step-by-step guide outlines the essential stages to build a reliable and user-centric IoT health app.
1. Define Clear Objectives and Use Cases
Before building your IoT health app, clarify the problems you want to solve. Ask yourself: Who is the target user—patients, doctors, or caregivers? Is the focus chronic disease management, fitness, or post-surgery care?
What health metrics matter most—heart rate, glucose levels, or activity tracking? Defining these objectives upfront helps shape app features, device selection, and data strategy, ensuring the product delivers real-world healthcare value.
2. Conduct Regulatory and Compliance Research
Healthcare is highly regulated, and failing to comply can result in severe legal consequences. Before development, study relevant laws like HIPAA, GDPR, or FDA guidelines, depending on your target market.
These regulations outline the guidelines for collecting, storing, and sharing sensitive health data. Ensuring compliance from the start not only builds user trust but also avoids costly rework later. A compliance-first mindset sets the foundation for safe and reliable app adoption.
3. Select IoT Devices and Sensors
The effectiveness of your health app depends on the reliability of IoT devices and sensors. Select wearable devices that can accurately track relevant health data such as steps, distance, heart rate, or sleep patterns.
Moreover, ensure compatibility between devices and the app to support seamless data integration. Choosing the right hardware ensures dependable data collection and user satisfaction.
4. Design System Architecture
Your system architecture is the backbone of an IoT-integrated health app. It should outline how devices, mobile apps, cloud services, and APIs interact. Decide whether you’ll use cloud-based or hybrid (cloud + edge) models for data processing.
Incorporate scalability to handle growing users and interoperability for smooth data exchange with healthcare systems. A well-structured architecture provides a secure, reliable foundation, ensuring your app can scale and adapt as healthcare needs evolve.
5. Develop Secure Data Management Strategy
Protecting patient data is one of the biggest responsibilities in healthcare apps. Implement strong encryption methods for data in transit and at rest, along with multi-level access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can view sensitive records.
Moreover, use secure cloud storage with backup and disaster recovery plans. Regularly conduct security audits to identify vulnerabilities. A robust data management strategy builds user trust and ensures compliance with HIPAA and GDPR.
6. Build the Application Interface
A well-designed interface is essential for user engagement. For patients, create an intuitive mobile app with real-time health dashboards, progress tracking, and medication reminders. For doctors or caregivers, design a web-based portal that displays critical insights, alerts, and reports.
Prioritize accessibility, minimal navigation, and simple design to ensure that users can easily interact with the app regardless of their technical expertise. Overall, effective UI/UX design ensures higher adoption and consistent use of your health app.
7. Development (Backend and IoT Integration)
The development stage focuses on building the backend that powers your IoT health app. This involves integrating IoT devices with APIs, managing data pipelines, and ensuring seamless connectivity between sensors, cloud storage, and the app.
Additionally, implement secure authentication methods, real-time data streaming, and efficient synchronization to handle large volumes of health information. A strong backend and robust IoT integration guarantee reliable performance, scalability, and accurate health data delivery.
8. Test for Accuracy and Reliability
Testing is critical to ensure your IoT health app functions effectively in real-world scenarios. Validate sensor accuracy by comparing device data with clinical standards. Conduct performance testing to evaluate response times, connectivity stability, and scalability under heavy data loads.
Security testing should identify vulnerabilities against cyberattacks. Involving healthcare professionals in the testing process adds credibility. Thorough testing guarantees that patients and doctors can rely on the app for accurate insights.
9. Launch and Continuous Monitoring
Once development and testing are complete, launch your app strategically—whether directly to app stores accessible to everyone or in pilot mode. After release, continuously monitor app performance, user feedback, and device connectivity to identify issues early.
Regular updates should address bugs, improve features, and enhance security. Ongoing monitoring ensures the app remains reliable, compliant, and valuable in a rapidly evolving healthcare environment where patient safety is paramount.
Dive into: How to Build an IoT App for Your Business
Future Trends in IoT and HealthCare Apps
The evolution of IoT in healthcare is driving innovations that make treatment more proactive and personalized. As devices become smarter and more interconnected, health apps are set to play a central role in improving accessibility, security, and efficiency. These trends highlight the direction of healthcare’s digital future.
1. AI-Powered Predictive Analytics
AI combined with IoT data is transforming how healthcare providers predict and prevent diseases. By analyzing patient data in real-time, predictive models can identify risks before they escalate. This proactive approach reduces in-patient visits and improves outcomes. It also shifts healthcare from being reactive to preventive.
- Detects patterns in patient data to forecast potential health issues.
- Provides early warnings for chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
- Delivers personalized preventive care recommendations based on lifestyle and history.
Explore more: Developing IoT Solutions with AI: Opportunities and Challenges
2. Voice-Enabled Health Assistants
AI voice assistants are making health apps more accessible and user-friendly. Patients can interact with apps hands-free, which is especially valuable for elderly users or those with limited mobility. These assistants provide reminders, answer questions, and connect patients with healthcare providers. The result is improved engagement and patient independence.
- Offers medication reminders and daily health check-ins via voice.
- Provides quick access to health information without navigating menus.
- Enhances accessibility for visually impaired or mobility-challenged patients.
3. 5G-Enabled Remote Healthcare
The rollout of 5G is a game-changer for IoT in healthcare. Its high speed and low latency enable real-time monitoring, telemedicine, and even remote surgeries. Patients and doctors can now exchange health data instantly, improving timely interventions. 5G ensures reliable connectivity for critical healthcare applications.
- Supports high-quality video consultations without lag.
- Enables real-time monitoring of patients through connected devices.
- Facilitates faster transmission of large health datasets for analysis.
4. Edge Computing in Healthcare Devices
Edge computing processes data closer to where it is collected, reducing reliance on the cloud. In healthcare, this means faster analysis and response times for critical alerts. Patients benefit from immediate feedback on their health, while providers get actionable insights quickly. It enhances both safety and efficiency.
- Reduces latency by processing data locally on devices or edge servers.
- Provides instant alerts for emergencies like irregular heart rhythms.
- Lessens dependence on cloud bandwidth for real-time functions.
5. Interoperability Standards Adoption
Healthcare systems often struggle with device compatibility, and interoperability standards aim to solve this. By adopting common frameworks, IoT health apps and devices can exchange data seamlessly. This makes integration with electronic health records (EHRs) smoother and enables holistic patient care. It also encourages wider adoption of IoT in healthcare ecosystems.
- Standardizes communication between devices from different manufacturers.
- Simplifies integration with hospital and clinic healthcare systems.
- Improves data consistency, reducing errors in patient health records.
Gamification in IoT-Enabled Health Apps: Driving Engagement and Promoting Healthy Habits

Gamification is a powerful technique in IoT health apps that transforms health monitoring and wellness routines into engaging and motivating experiences. Integrating gamification in IoT apps makes tracking health data and achieving goals interactive and fun.
Key gamification features in IoT Health Apps include:
- Personalized Fitness Challenges: Adapting goals and milestones to users’ unique health data and progress to keep motivation high through achievable personalized targets.
- Badges & Achievements: Digital rewards for milestones like consistent step tracking or medication adherence that encourage continued participation and celebrate success.
- Leaderboards: Encouraging friendly competition within user communities by comparing progress and fostering social motivation.
- Progress Tracking: Providing real-time visual feedback via progress bars and notifications to keep users informed and engaged in their health journey.
- Social Sharing and Community Support: Enabling users to share achievements and participate in groups for encouragement, accountability, and motivation.
- Narrative and Virtual Adventures: Integrating story-driven workouts or mission-based health quests that make routine tasks immersive, fun, and mentally stimulating.
By combining health data from IoT devices with gamification, these apps promote long-term adherence to healthy habits and support proactive wellness, effectively transforming healthcare into an interactive journey.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT in health apps is redefining the way patients, doctors, and caregivers approach healthcare. From wearables that track daily activity to smart devices monitoring chronic conditions, these apps provide real-time data, personalized insights, and seamless connectivity across healthcare systems. IoT-enabled health apps not only empower individuals to take control of their well-being but also support doctors in making informed, data-driven decisions.
While challenges like data privacy, interoperability, and device reliability remain, the ongoing advancements in AI, 5G, and smart wearables promise a future of more connected, proactive, and preventive healthcare. The journey from wearables to wellness has only just begun.


